

It’s almost 30 years old. Not to knock cURL, it’s a staple for sure.
HTTPie and xh claim to have a more intuitive UX. If the functionality is comparable, I choose tools written in memory-safe languages by default.
Professional software engineer, musician, gamer, stoic, democratic socialist


It’s almost 30 years old. Not to knock cURL, it’s a staple for sure.
HTTPie and xh claim to have a more intuitive UX. If the functionality is comparable, I choose tools written in memory-safe languages by default.


xh is a nice modern alternative.


deleted by creator


Organizationally, you don’t want your API handler to care about implementation details like database queries. All DB interaction should be abstracted into a separate layer.
Generally API handlers only care about injecting any “global” dependencies (like a database object), extracting the request payload, and dispatching into some lower-level method.
None of this requires generic code. It’s just about having a clear separation of concerns, and this can lead to more reusable and testable code.


that’s a git problem, not Windows.
I use Git, and I don’t use Windows. I have no problems. Sounds like… a Windows problem?


You are never guaranteed to be able to do anything during a crash. You are better off handling these kinds of edge cases in a recovery phase during the start of your app.


Has a simple backup and migration workflow. I recently had to backup and migrate a MediaWiki database. It was pretty smooth but not as simple as it could be. If your data model is spread across RDBMS and file, you need to provide a CLI tool that does the export/import.
Easy to run as a systemd service. This is the main criteria for whether it will be easy to create a NixOS module.
Has health endpoints for monitoring.
Has an admin web UI that surfaces important configuration info.
If there are external service dependencies like postgres or redis, then there needs to be a wealth of documentation on how those integrations work. Provide infrastructure as code examples! IME systemd and NixOS modules are very capable of deploying these kinds of distributed systems.
This type of shit makes me aware that there really are devs that don’t care about efficiency and will spend weeks on some really novice shit because their tools and skills are bad.


Silverbullet is nice


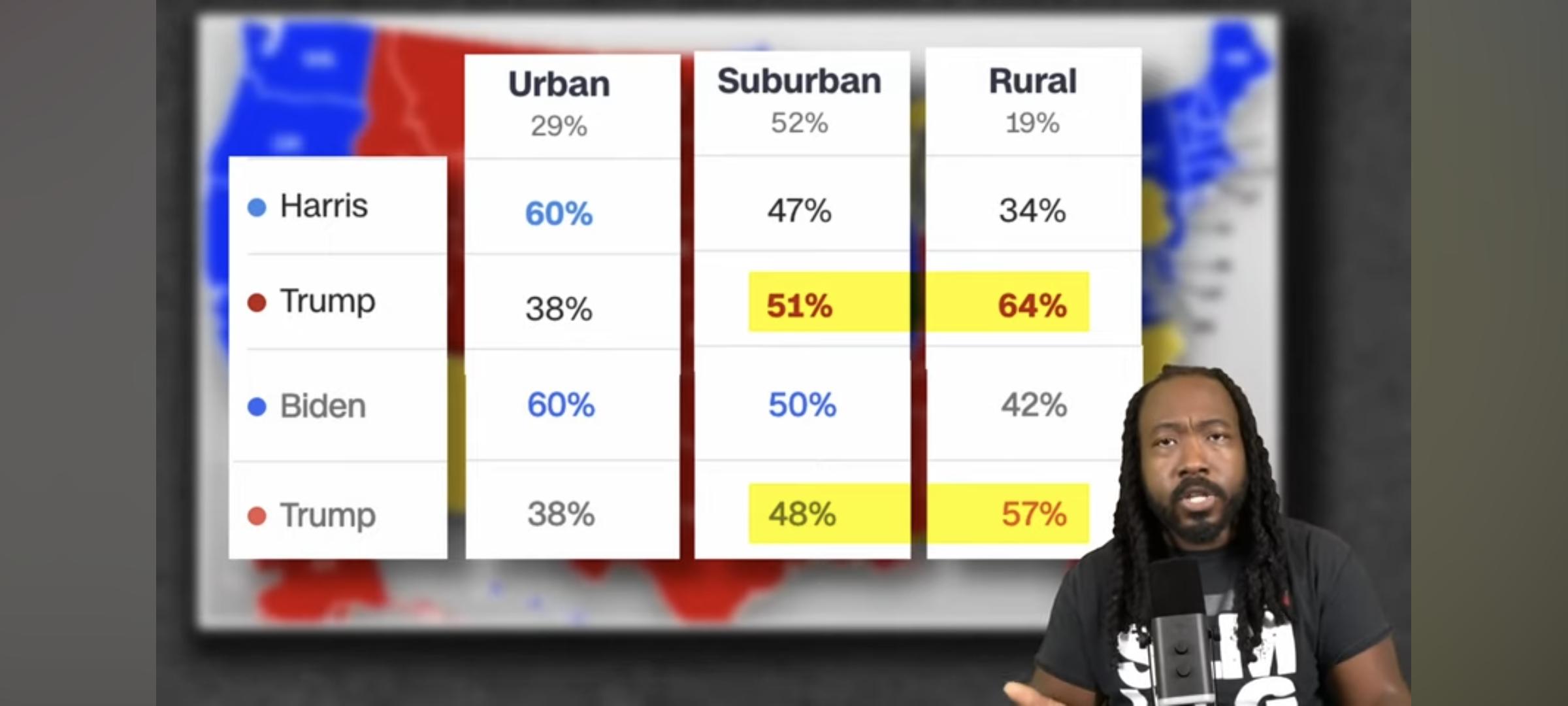
The most important part IMO.


Cool so this article calls out various types of coupling and offers no strategies for managing it.
Waste of time.


I like AdGuard Home myself.


Wireguard is p2p.
EDIT: I guess the point is it’s doing peer discovery without static public IPs or DNS. Pretty cool!


anything else > python > JS


This makes me so nervous about how AI is going to influence children and adolescents of the coming generations. From iPad kids to AI teens. They’ll be at a huge risk of dissociation from reality.
Agreed.
And sometimes code is not the right medium for communicating domain knowledge. For example, if you are writing code the does some geometric calculations, with lot of trigonometry, etc. Even with clear variable names, it can be hard to decipher without a generous comment or splitting it up into functions with verbose names. Sometimes you really just want a picture of what’s happening, in SVG format, embedded into the function documentation HTML.


There are plenty of good resources online. Here are some topics you probably wouldn’t see in an intro algos course (which I’ve actually used in my career). And I highly recommend finding the motivation for each of these in application rather than just learning them abstractly.


It’s almost like Nintendo wanted to make as much money as possible in court.
Sir, I estimate the project will be completed in 135 days and 11 hours.
This would be more believable if Elon paid his cloud bills.